Beijing, February 2026 — In the AI era, where computing power equates to productivity, the response speed of storage systems has become a critical variable in determining large model training efficiency. In the recently released MLPerf™ Storage v2.0 benchmarks, Memblaze, in collaboration with industry partners, achieved multiple top rankings with a massive aggregate data bandwidth of 513GB/s. This milestone stems not only from breakthroughs in underlying hardware but also from the high-efficiency synergy across the entire storage architecture.
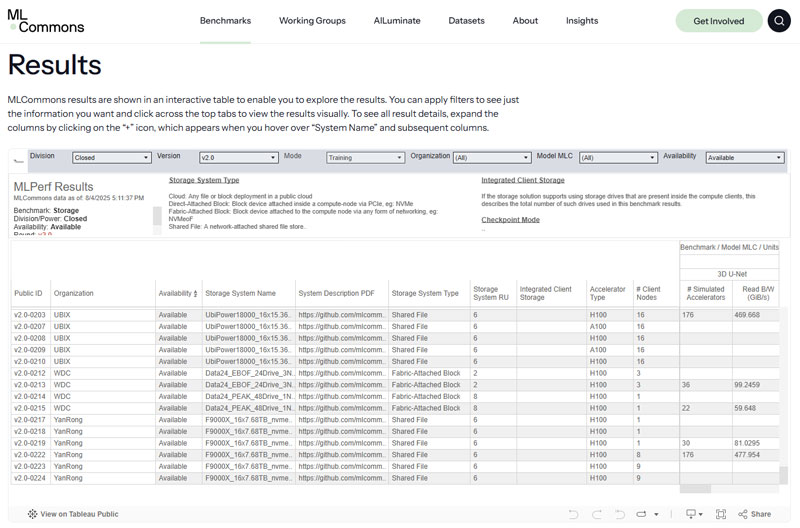
MLPerf Storage v2.0 Results (From MLCommons Website)
MLPerf™ Storage, governed by the global authority MLCommons, is widely regarded as the "Olympics" of AI performance. Compared to v1.0, the v2.0 update introduces more rigorous testing dimensions: it requires multiple experimental repetitions to verify average performance, implements strict environment validation, and introduces the critical Checkpoint save/load phase. These evolutions are designed to eliminate "burst peak" interference, revealing the true resilience and sustained output of a storage system under prolonged, high-pressure, and complex AI workloads.
For enterprise SSD manufacturers, beyond large-scale storage architectures, it is essential to return to raw local storage performance. Testing a single SSD in its simplest configuration provides a transparent view of its native capabilities under identical workloads.
"We cannot predict which servers or system configurations our users will choose. Our mission is to provide the highest possible SSD performance to serve as a rock-solid, reliable foundation for any AI training task."
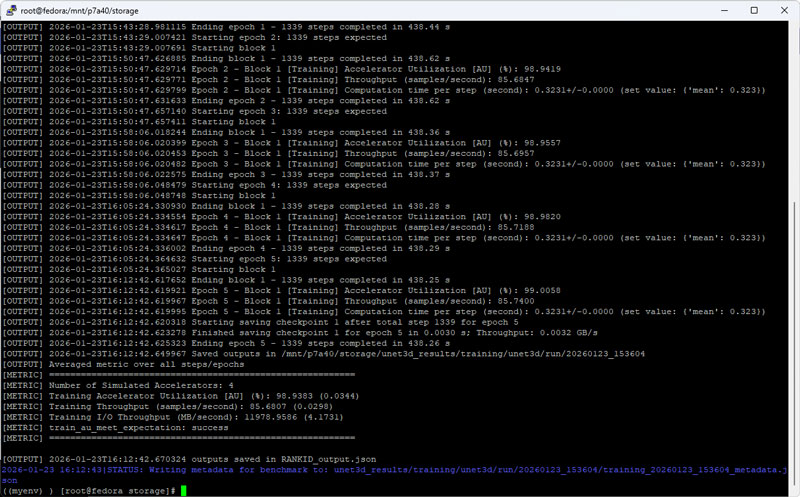
MLPerf Storage v2.0 3D-UNet Test Result
The following benchmarks were conducted using a single PBlaze7 7A40 7.68TB PCIe 5.0 SSD on a standard 2U server equipped with dual Xeon 8457C processors and 1TB of system RAM, running Fedora with XFS. The dataset was set above 5TB to minimize system memory caching effects, strictly adhering to MLPerf™ Storage v2.0 specifications.
3D-UNet (Medical Imaging) requires immense bandwidth. With a batch size of 7, a single NVIDIA H100 GPU processes data every 0.323s, requiring at least 2.85GB/s of sustained throughput to maintain >90% utilization.
In a 4-H100 GPU simulation, the PBlaze7 7A40 delivered a stable 11,978 MB/s, achieving a GPU utilization of 98.94%. This result outperforms official data from Vendor A (11,450 MB/s) and Vendor B (11,568 MB/s). In an 8-A100 GPU setup, the drive reached an even higher 12,208 MB/s.
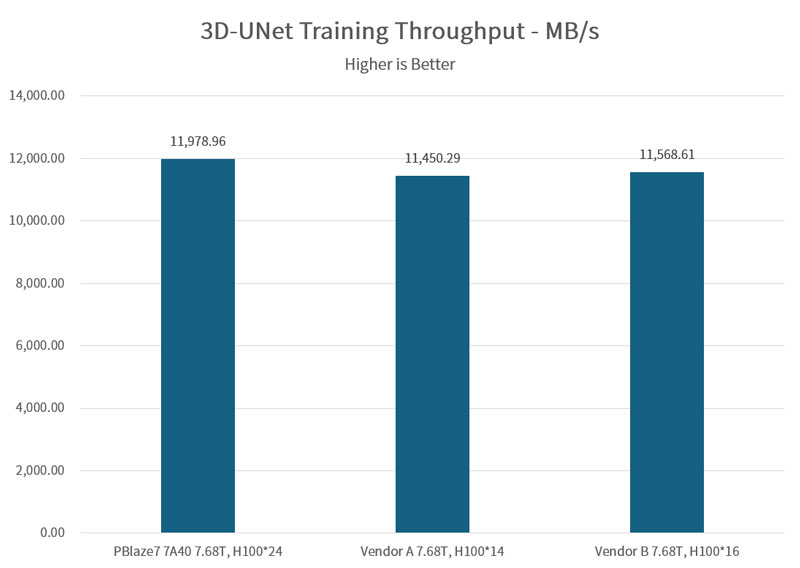
ResNet-50 demands high-frequency file index processing and real-time decompression via TensorFlow, testing an SSD’s random read latency.
In a 64-H100 GPU environment, the PBlaze7 7A40 provided 12,284 MB/s (98.49% utilization). When pushed to 72 GPUs (simulating an additional 8-GPU node), bandwidth climbed to 13,119 MB/s while maintaining over 93% utilization.
Comparative Edge: At the same 64-H100 load, the PBlaze7 7A40 significantly exceeded the 11,562 MB/s mark set by industry peer Vendor B.
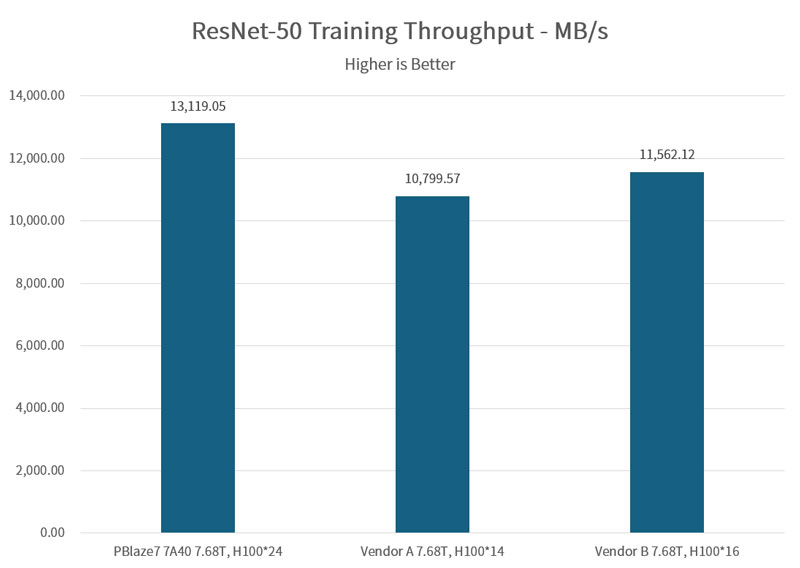
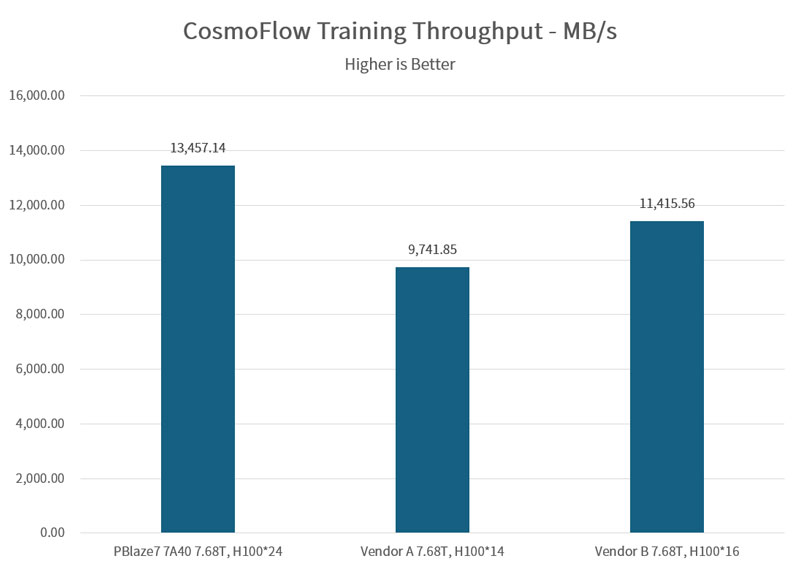
CosmoFlow utilizes 1.94 million samples, each averaging just 2.8MB. This creates a massive I/O request load for metadata and file retrieval.
While the MLPerf™ passing threshold is 70% GPU utilization, the PBlaze7 7A40 powered 16 H100 GPUs at over 90% utilization. It supported up to 24 H100 GPUs while maintaining 74.35% utilization at a bandwidth of 13,457 MB/s.
In LLM training (like Llama-405B), GPU resources sit idle during Checkpoint save/load cycles. Every second saved is a direct reduction in compute cost.
The PBlaze7 7A40 achieved a save speed of 8.43 GB/s and a load speed of 7.45 GB/s, completing save/recovery operations for the massive model in just 6 and 7 seconds, respectively.
Compared to legacy PCIe 4.0 SSDs, which often see save times double due to bandwidth bottlenecks, the PBlaze7 7A40 significantly reduces non-computing time, maximizing the Return on Investment (ROI) for AI clusters.
The MLPerf™ Storage v2.0 results confirm that the PBlaze7 7A40 PCIe Gen5 SSD is a premier infrastructure component for AI. By drastically reducing "I/O Wait" times across high-throughput, high-concurrency, and metadata-heavy workloads, Memblaze continues to provide the "storage backbone" required for the next generation of Large Language Models.